Boost C++ Libraries学习 - Geometry
系列文章
《计算几何——算法与应用(第三版)》学习笔记1 - 扫描线(第1-4章)
《计算几何——算法与应用(第三版)》学习笔记2 - 空间索引(第5-7章)
番外篇
计算几何 - C++ 库的调研
-> Boost C++ Libraries学习 - Geometry
Boost C++ Libraries学习 - Boost.Polygon (GTL)
参考 Boost 官方手册
Boost.Geometry contains a dimension-agnostic, coordinate-system-agnostic and scalable kernel, based on concepts, meta-function and tag dispatching. On top of that kernel, algorithms are built: area, length, perimeter, centroid, convex hull, intersection (clipping), within (point in polygon), distance, envelope (bounding box), simplify, transform, and much more. The library supports high precision arithmetic numbers, such as ttmath.
设计原理
Boost 库作为 C++ 中非常常用的库,学习其中的设计原理是对自身的设计能力提高非常有用的。
计算距离的例子
看一个使用自定义点结构计算两点之间的距离的例子,最简单的实现方式如下:
1 | struct mypoint { |
计算距离这个需求其实是通用的,如果从库开发者的角度来说,这段代码有如下的问题:
- 应该支持任意的“点”概念的结构或类。
- 应该不局限于二维。
- 应该不局限于笛卡尔坐标系(Cartesian coordinate system)。
- 距离概念不止存在于两个点之间,传入任意几何图形的组合也应能计算距离。
double的精度有时不够。- 计算平方根代价相对较大,而且如果是距离比较,绝对的距离不是很重要。
详细修改步骤在这里
解决以上问题的方法:
- 使用模板,就可以支持其他“点”了。
- 使用 Traits 扩展为维度无关以及坐标类型无关。
- 使用 Traits 扩展不同坐标系。
- 不同几何之间计算距离,使用 tag dispatching 技术。
使用Boost.Geometry
安装
MacOS 下,使用 homebrew 安装:brew install boost
建立 CMake 工程,并在 CMakeLists.txt 文件中加入以下内容:
1 | find_package(Boost COMPONENTS system filesystem REQUIRED) |
使用
1 |
|
空间索引(R-Tree)
目前来说,Boost.Geometry 库唯一实现的数据结构是 R-Tree。
TODO: R-Tree 可视化
元素操作
R-Tree 类长这样:
1 | rtree<Value, |
其中:
- Value: 被存储在容器中的数据类型。
- Parameters: 参数类型,指明使用的插入/划分算法。
- IndexableGetter: 函数对象,让 R-Tree 能够理解如何将 Value 转换成 Indexable 对象。
- EqualTo: 用来比较 Value 的函数对象。
- Allocator: 创建节点时的申请内存方法。
Indexable 对象是符合 Point, Box 或者 Segment 观念的几何对象。
Value 也可以是 pair 或者 tuple,但需要把 Indexable 对象放在这些数据的第一个。
支持三种算法:
- Linear:
index::rtree< Value, index::linear<16> > rt; - Quadratic:
index::rtree< Value, index::quadratic<16> > rt; - R*-tree:
index::rtree< Value, index::rstar<16> > rt;
想要将算法参数在运行时传入 R-Tree,使用下面的写法:
1 | index::rtree<Value, index::dynamic_linear> rt(index::dynamic_linear(16)); |
可以使用 R-Tree 中的方法来插入、删除,也可以使用 index:: 中的函数插入、删除。可以插入、删除一个元素,也可以范围操作,具体参考这里。
查询
查询结果要符合一些谓词(predicates)描述,有三种谓词:
- 空间谓词(spatial predicates)
- 距离谓词(distance predicates)
- 自定义谓词(user-defined unary predicate)
查询的写法如下:
1 | std::vector<Value> returned_values; |
由于查询结果一般是用来遍历的,有一种方便的写法(使用|):
1 | Box box_region(...); |
空间查询
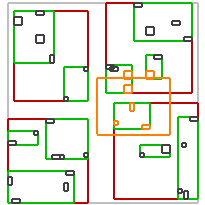
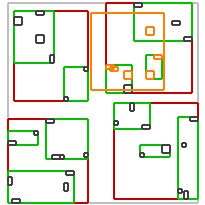
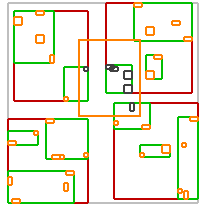
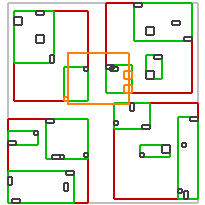
不同谓词的效果如下:
| intersects(Box) | covered_by(Box) | disjoint(Box) | overlaps(Box) | within(Box) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
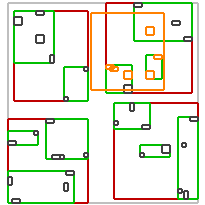 |
| intersects(Segment) | intersects(Box) | disjoint(Box) | intersects(Box) | disjoint(Box) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
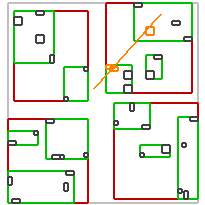 |
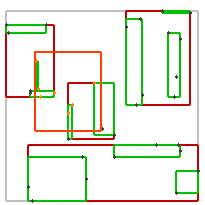 |
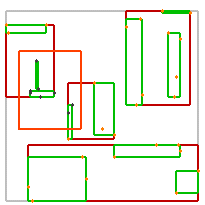 |
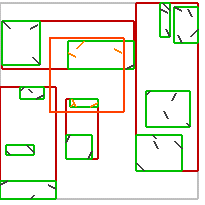 |
 |
使用如下代码:
1 |
|
得到输出:
1 | --- |
可视化:
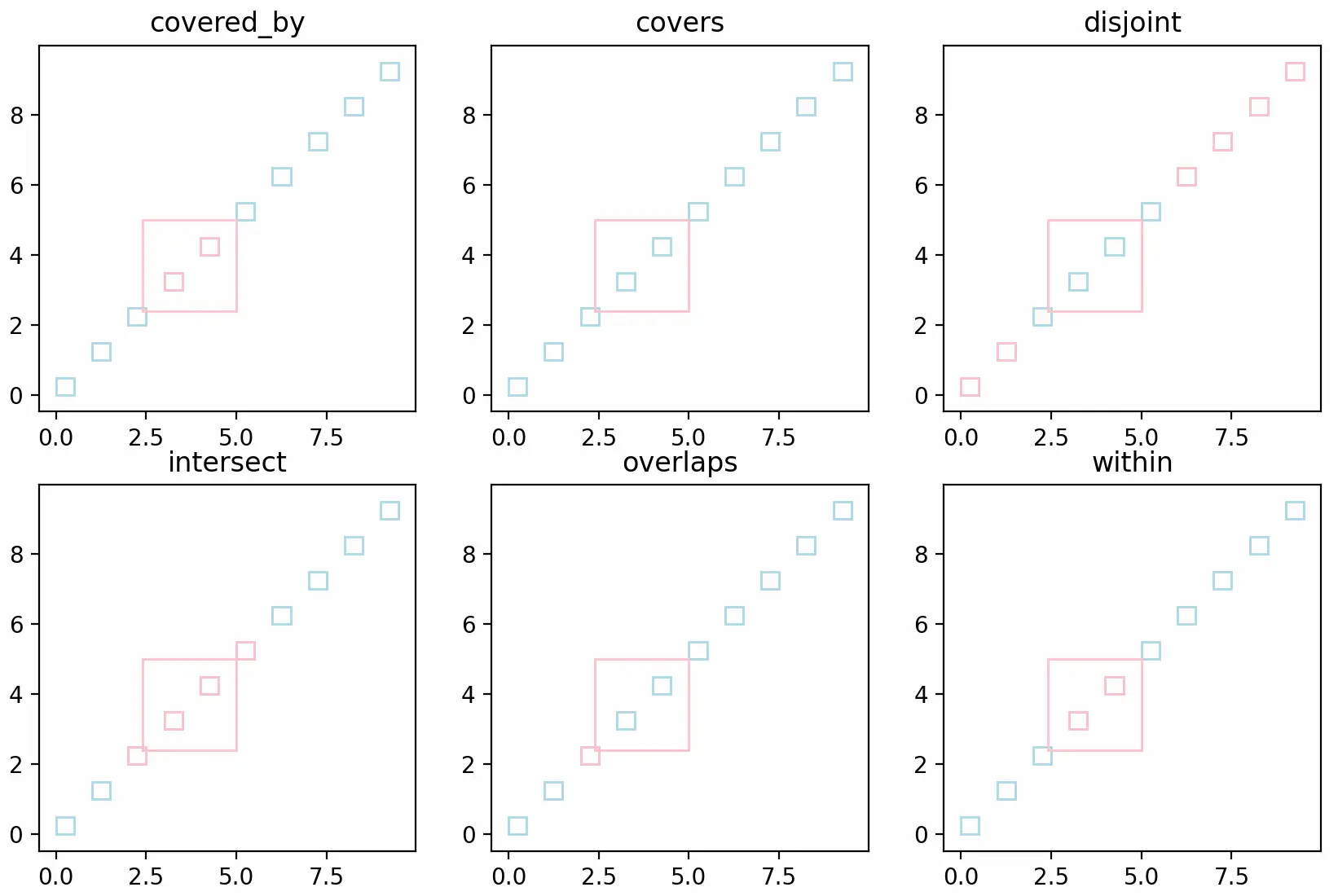
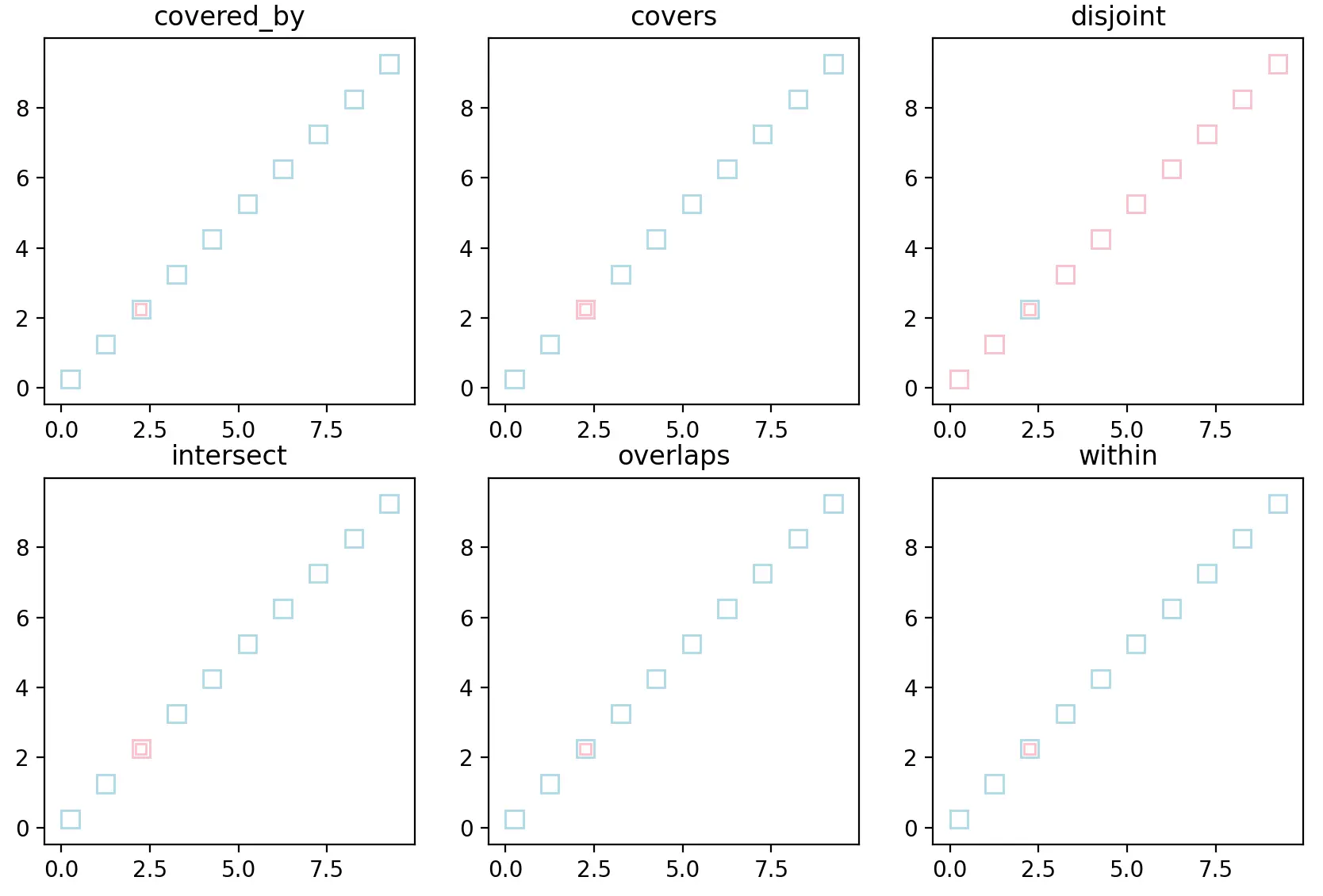
调小查询矩形后的可视化结果:
附上可视化使用的 python 代码:
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- |
如果要使用自定义的谓词,用下面的写法:
1 | rt.query(index::intersects(box) && index::satisfies([](Value const& v) { return v.is_red(); }), |