说起来,贪吃蛇游戏好像贯穿了我的编程学习之路。
大一时候,用单片机点亮了一个8x8的LED阵列,配合上下左右四个按键,在C51平台写了自己所理解的贪吃蛇版本。以至于大二当上了光协技术部部长时也把“调通我提供的贪吃蛇框架代码、自己再实现部分特殊功能”作为学校电子竞赛软件类的题目用来“迫害”学弟学妹们。
之后参加电赛,暑假准备期间,为了让到正式比赛时我们的作品能有很好的界面以及交互,开始调一块4.7寸的电容屏,在STM32平台上编写自己的图形框架。框架编写得很顺利,所以开始写程序玩,又想到了贪吃蛇!可是现在只有触屏,要是照着手机的策略,加上虚拟按键搓屏幕,总觉得不够优雅。要不让贪吃蛇自己动起来吧!想了一些方案,当时也还不知道有A*算法,用DFS写出了自己的第一个自动贪吃蛇版本。角色互换,玩家通过触屏控制食物的生成,计算机来控制蛇寻找食物并吃掉。
学习python的过程中,接触到了pygame,又把之前在MCU的自动贪吃蛇用python实现了一遍。
工作的时候,为了提升自己的工作效率,下班后开发了几个开发工具(后来这三个工具成了组里面以至于部门里面绝对的流行哈哈哈,以后可以聊聊这个话题)。开发得差不多了,就想着往里面添加彩蛋,毕竟这些程序是我自己的,不是公司里面的。这时候在用得最频繁的上位机上面实现了C#版本的自动贪吃蛇,引入了A*算法,并且图形也不再是一个个方块了,而是使用折线来绘制蛇身,可以连续移动。
考研期间有花一部分时间用来学unity,又想到了这个项目,于是想做一个最终的版本,这个版本会有卓越的性能优化,也有简洁漂亮的外观。也就是今天要讲述的版本。
网格
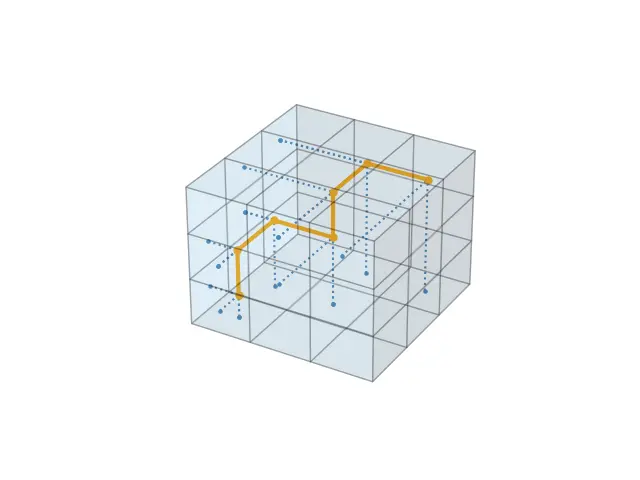
在使用A*进行寻路之前,得将地图进行网格化,网格的大小决定了寻路的精度。另一方面正好经典的贪吃蛇游戏是在网格上进行游玩的。
若遇到连续地图的游戏,可以先对地图进行预处理:即以一定的间隔对地图进行采样,如果以采样点为中心的一定范围内出现了不可达区域,则将该采样点对应的网格设置为不可行走。
网格划分
在场景中添加空物体,起名为GridController,为其添加GridController.cs脚本。
其中与建立网格相关代码如下:GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 private void Awake (){ CreateGrid(); RefreshGrid(); }
CreateGrid方法用来创建网格节点。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public Coord mapSize = new (10 , 10 );AStar.Node[,] grid; void CreateGrid (){ grid = new AStar.Node[mapSize.x, mapSize.y]; for (int x = 0 ; x < mapSize.x; x++) { for (int y = 0 ; y < mapSize.y; y++) { grid[x, y] = new AStar.Node(true , GridCoordToWorldPosition(x, y), x, y); } } AdjustWalls(mapSize.x, mapSize.y); }
RefreshGrid方法会清除上一次使用A*算法时对grid带来的改变。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void RefreshGrid (){ for (int x = 0 ; x < mapSize.x; x++) { for (int y = 0 ; y < mapSize.y; y++) { AStar.Node currentNode = grid[x, y]; currentNode.walkable = true ; currentNode.gCost = 0 ; currentNode.hCost = 0 ; currentNode.parent = null ; } } }
AdjustWalls方法中,walls和background都是在编辑器中设置,当每次网格变化时,该方法会调整边界以匹配网格。后续发现使用专门的相机来渲染背景会比现在这个方法优雅很多,等“贪吃蛇”章节再讲。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public Transform[] walls;public Transform background;public void AdjustWalls (int sizeX, int sizeY{ float wallPositionX = sizeX / 2f + .5 f; walls[0 ].position = Vector3.left * wallPositionX; walls[1 ].position = Vector3.right * wallPositionX; Vector3 tallWallScale = Vector3.up * (sizeY - 1 ) + Vector3.one; walls[0 ].localScale = tallWallScale; walls[1 ].localScale = tallWallScale; float wallPositionY = sizeY / 2f + .5 f; walls[2 ].position = Vector3.up * wallPositionY; walls[3 ].position = Vector3.down * wallPositionY; Vector3 fatWallScale = Vector3.right * (sizeX + 1 ) + Vector3.one; walls[2 ].localScale = fatWallScale; walls[3 ].localScale = fatWallScale; background.localScale = tallWallScale - Vector3.up + fatWallScale - 3 * Vector3.right; }
坐标转换
坐标转换分为两种,一种是网格坐标和世界坐标的互相转换,另一种是网格坐标和一维坐标的转换。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public Coord WorldPositionToGridCoord (Vector3 worldPos ){ int coordX = Mathf.RoundToInt(worldPos.x / gridSize + (mapSize.x - 1 ) / 2f ); int coordY = Mathf.RoundToInt(worldPos.y / gridSize + (mapSize.y - 1 ) / 2f ); return new (coordX, coordY); } public Vector3 GridCoordToWorldPosition (Coord coord ){ return GridCoordToWorldPosition(coord.x, coord.y); } public Vector3 GridCoordToWorldPosition (int x, int y{ float worldX = x * gridSize - (mapSize.x - 1 ) * gridSize / 2f ; float worldY = y * gridSize - (mapSize.y - 1 ) * gridSize / 2f ; return new Vector3(worldX, worldY, 0 ); } public int CoordToIndex (int x, int y{ return y * mapSize.x + x; } public int CoordToIndex (Coord coord ){ return CoordToIndex(coord.x, coord.y); } public Coord IndexToCoord (int idx{ return new Coord(idx % mapSize.x, idx / mapSize.x); }
其中Coord是一个整数坐标的类:GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 [System.Serializable ] public struct Coord{ public int x; public int y; public Coord (int _x, int _y { x = _x; y = _y; } public static bool operator ==(Coord a, Coord b) { return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y; } public static bool operator !=(Coord a, Coord b) { return !(a == b); } public override bool Equals (object obj { return base .Equals(obj); } public override int GetHashCode () { return base .GetHashCode(); } public static Coord operator +(Coord a, Vector2 b) { return new (a.x + (int )b.x, a.y + (int )b.y); } public static Coord operator +(Coord a, Coord b) { return new (a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y); } }
并查集
A*算法虽然高效,但是每次都需要刷新所有网格节点以清除A*算法的临时数据,而且如果两个节点之间不存在路径,A*算法需要将起点所在连通域里面所有的节点都遍历完。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public UFSet set { get ; private set ; }void CreateGrid (){ set = new (gridCount); } public void RefreshSet (){ set .Init(); for (int x = 0 ; x < mapSize.x; x++) { for (int y = 0 ; y < mapSize.y; y++) { if (grid[x, y].walkable) { Coord currentCoord = new Coord(x, y) + Vector2.left; if (IsCoordInsideGrid(currentCoord) && grid[currentCoord.x, currentCoord.y].walkable) { set .Union(CoordToIndex(x, y), CoordToIndex(currentCoord)); } currentCoord = new Coord(x, y) + Vector2.up; if (IsCoordInsideGrid(currentCoord) && grid[currentCoord.x, currentCoord.y].walkable) { set .Union(CoordToIndex(x, y), CoordToIndex(currentCoord)); } } } } } public bool IsConnected (AStar.Node startNode, AStar.Node targetNode ){ return set .Find(CoordToIndex(startNode.gridCoord)) == set .Find(CoordToIndex(targetNode.gridCoord)); } bool IsCoordInsideGrid (Coord coord ){ return IsCoordInsideGrid(coord.x, coord.y); } bool IsCoordInsideGrid (int x, int y{ if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= mapSize.x || y >= mapSize.y) return false ; return true ; }
并查集的类需要自己编写,这里用了一些平衡的方式,使得并查集搜索时不至于太大的深度。UFSet.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class UFSet { public int [] parent { get ; private set ; } private int [] rank; public UFSet (int n { parent = new int [n]; rank = new int [n]; Init(); } public void Init () { for (int i = 0 ; i < parent.Length; i++) { parent[i] = i; rank[i] = 1 ; } } public bool Union (int a, int b { int rootA = Find(a); int rootB = Find(b); if (rootA == rootB) return false ; if (rank[rootA] < rank[rootB]) { parent[rootA] = rootB; } else { parent[rootB] = rootA; if (rank[rootA] == rank[rootB]) rank[rootA]++; } return true ; } public int Find (int p { if (parent[p] != p) parent[p] = Find(parent[p]); return parent[p]; } public bool IsConnected (int a, int b { return parent[a] == parent[b]; } }
提供的服务
GridController中会处理玩家输入,即让玩家在网格中任意位置点击鼠标时可以生成食物。为了让程序自动运行时也能有进展,GridController中也实现了自动生成食物的功能。使用洗牌算法来随机排列可行走的网格,当没有食物时从随机排列的列表中选择第一个作为食物生成的节点。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 public Food foodPrefab;[HideInInspector ] public List<Food> foods;Queue<AStar.Node> shuffledWalkableNodes; private void Update (){ Vector3 mousePos = Camera.main.ScreenToWorldPoint(Input.mousePosition); cursor.transform.position = new Vector3(mousePos.x, mousePos.y, 0 ); if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0 )) { Coord foodCoord = WorldPositionToGridCoord(cursor.position); if (IsCoordInsideGrid(foodCoord)) { AStar.Node foodNode = GetNodeFromCoord(foodCoord); if (foodNode.walkable) { CreateFood(cursor.position); } } } } void CreateFood (Vector3 position ){ Food newFood = Instantiate(foodPrefab, position, Quaternion.identity); newFood.transform.SetParent(transform, false ); newFood.OnFoodAte += OnFoodAte; newFood.SetNode(GetNodeFromWorldPosition(position)); foods.Add(newFood); } void OnFoodAte (Food food ){ foods.Remove(food); Destroy(food.gameObject); } public void RefreshWalkableList (){ List<AStar.Node> walkableNodes = new (); for (int x = 0 ; x < mapSize.x; x++) { for (int y = 0 ; y < mapSize.y; y++) { if (grid[x, y].walkable) walkableNodes.Add(grid[x, y]); } } shuffledWalkableNodes = new Queue<AStar.Node>(Utility.ShuffleArray(walkableNodes.ToArray())); if (autoGenerateFood && foods.Count == 0 ) { CreateFood(GetRandomWalkableNode().worldPosition); } }
其他类有时需要根据各种方式获得一个(些)网格节点,GridController中应该创建对应的方法。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public AStar.Node GetNode (Coord coord ) { return grid[coord.x, coord.y]; } public AStar.Node GetRandomWalkableNode () { AStar.Node randomNode = shuffledWalkableNodes.Dequeue(); shuffledWalkableNodes.Enqueue(randomNode); return randomNode; } public AStar.Node[] GetNeighbours (AStar.Node node ) { List<AStar.Node> neighbours = new List<AStar.Node>(); for (int x = -1 ; x <= 1 ; x++) { for (int y = -1 ; y <= 1 ; y++) { if ((x == 0 || y == 0 ) && x != y) { Coord coordDelta = new (x, y); Coord checkCoord = node.gridCoord + coordDelta; if (IsCoordInsideGrid(checkCoord)) { neighbours.Add(grid[checkCoord.x, checkCoord.y]); } } } } return neighbours.ToArray(); } public AStar.Node GetNodeFromCoord (Coord coord ) { if (!IsCoordInsideGrid(coord)) return null ; return grid[coord.x, coord.y]; } public AStar.Node GetNodeFromCoord (int x, int y { if (!IsCoordInsideGrid(x, y)) return null ; return grid[x, y]; } public AStar.Node GetNodeFromWorldPosition (Vector3 position ) { return GetNodeFromCoord(WorldPositionToGridCoord(position)); }
网格大小在UI中动态可调,调整时需要重建网格,也需要调整网格边界的显示。GridController.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void SetMapSize (int x, int y{ if (x < minMapSize.x) x = minMapSize.x; if (y < minMapSize.y) y = minMapSize.y; mapSize.x = x; mapSize.y = y; CreateGrid(); }
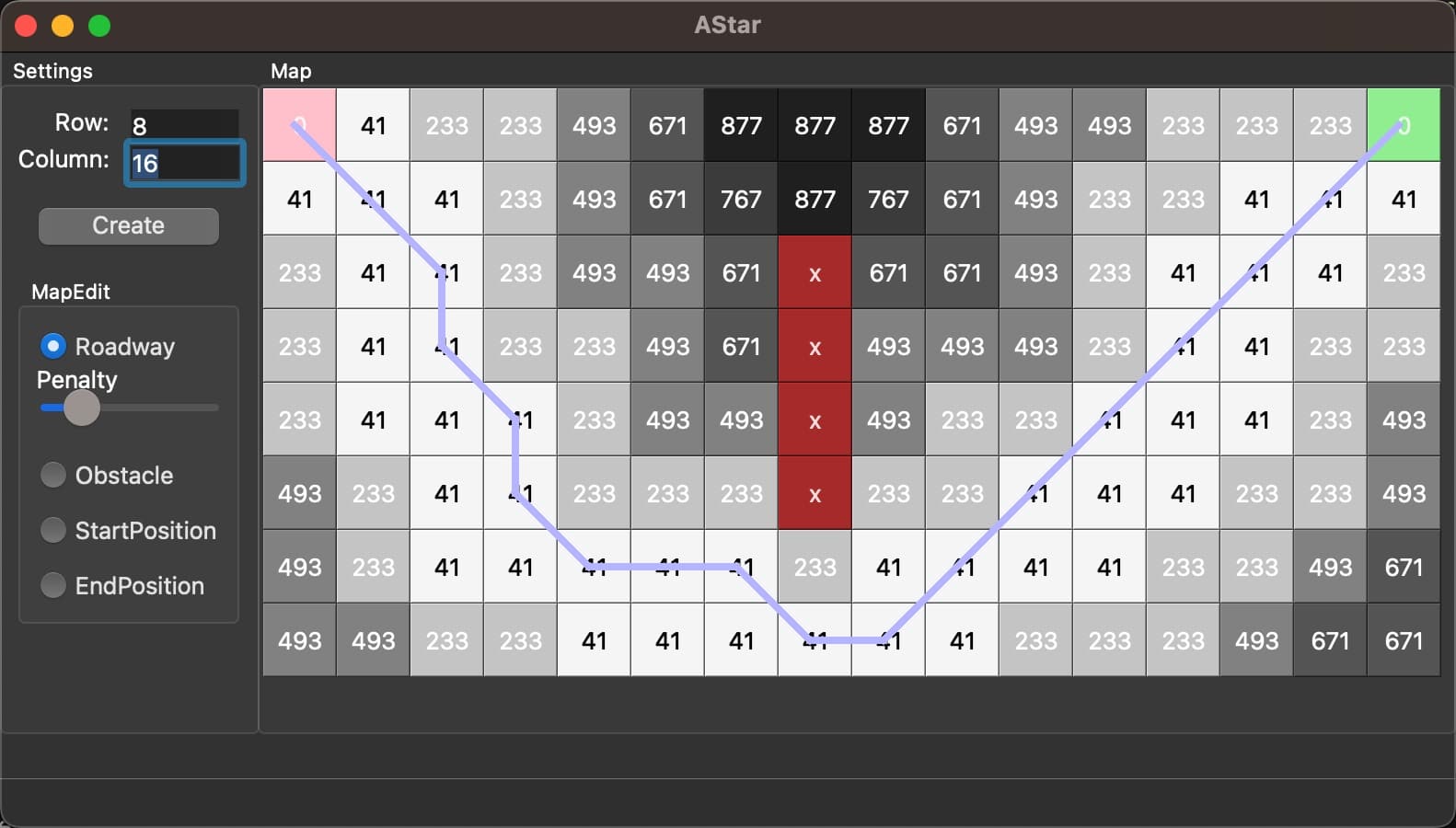
A*
去搜索A*算法的话,很多教程一上来就开始推导运行过程,不先讲为什么这么推导,导致我开始学A*的时候感到特别困惑。
已经知道的代价。即从起点到当前节点已经走过的路线长度。
未来可能会有的代价。用“猜”的,假设从当前节点到目标节点没有障碍,代价会是多少。
知道启发函数是怎么回事之后我们就可以开始遍历节点了。从起点开始,计算其四周节点的代价,并把那些节点放到一个“池子”里面去,之后每次都从池子里面捞出来代价最小的节点,继续计算其周围节点的代价。
至于算法优化,有如下几点细节:
计算当前节点的周围节点的代价值时,如果需计算的节点原先就已经算过代价值,而当前算出来的代价值比原先的小,说明这个节点从当前节点过去路径会更短一些,应当刷新其父节点和代价值。
我们之前说“池子”的时候,有提到每次需要从中找出代价最小的节点用来计算,而小根堆有很高效的寻找最小值元素的特性,所以将“池子”用小根堆来组织。
算法实现
定义算法所需要的节点类,其中IHeapItem是用来后续实现堆时能够让堆接收自定义的AStar.Node类作为堆中的元素。AStar.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Node : IHeapItem <Node >{ public bool walkable; public Vector3 worldPosition; public GridController.Coord gridCoord; public int gCost; public int hCost; public int fCost { get { return gCost + hCost; } } public Node parent; int heapIndex; public Node (bool _walkable, Vector3 _worldPos, int _gridX, int _gridY { walkable = _walkable; worldPosition = _worldPos; gridCoord = new (_gridX, _gridY); } public int HeapIndex { get { return heapIndex; } set { heapIndex = value ; } } public int CompareTo (Node nodeToCompare ) { int compare = fCost.CompareTo(nodeToCompare.fCost); if (compare == 0 ) compare = hCost.CompareTo(nodeToCompare.hCost); return -compare; } }
寻路算法的实现如下:AStar.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 GridController grid; private void Awake (){ grid = GetComponent<GridController>(); } public Node[] FindPath (Node startNode, Node targetNode ){ Heap<Node> openSet = new Heap<Node>(grid.gridCount); HashSet<Node> closedSet = new HashSet<Node>(); openSet.Add(startNode); while (openSet.Count > 0 ) { Node currentNode = openSet.RemoveFirst(); closedSet.Add(currentNode); if (currentNode == targetNode) { return RetracePath(startNode, targetNode); } foreach (Node neighbour in Utility.ShuffleArray(grid.GetNeighbours(currentNode))) { if (!neighbour.walkable || closedSet.Contains(neighbour)) continue ; int newMovementCostToNeighbour = currentNode.gCost + GetDistance(currentNode, neighbour); if (newMovementCostToNeighbour < neighbour.gCost || !openSet.Contains(neighbour)) { neighbour.gCost = newMovementCostToNeighbour; neighbour.hCost = GetDistance(neighbour, targetNode); neighbour.parent = currentNode; if (!openSet.Contains(neighbour)) { openSet.Add(neighbour); } } } } return null ; } int GetDistance (Node nodeA, Node nodeB ){ return Mathf.Abs(nodeA.gridCoord.x - nodeB.gridCoord.x) + Mathf.Abs(nodeA.gridCoord.y - nodeB.gridCoord.y); }
输出寻得的路径的代码如下:AStar.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Node[] RetracePath (Node startNode, Node endNode ) { List<Node> path = new List<Node>(); Node currentNode = endNode; while (currentNode != startNode) { path.Add(currentNode); currentNode = currentNode.parent; } path.Reverse(); return path.ToArray(); }
堆
C#中没有可以使用的现成的堆,需要自己编写。思路是将堆编写为模板类,要求其元素需实现IHeapItem接口。Heap.cs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 public class Heap <T > where T : IHeapItem <T >{ T[] items; int currentItemCount; public Heap (int maxHeapSize { items = new T[maxHeapSize]; } public void Add (T item ) { item.HeapIndex = currentItemCount; items[currentItemCount] = item; SortUp(item); currentItemCount++; } public T RemoveFirst () { T firstItem = items[0 ]; currentItemCount--; items[0 ] = items[currentItemCount]; items[0 ].HeapIndex = 0 ; SortDown(items[0 ]); return firstItem; } public void UpdateItem (T item ) { SortUp(item); SortDown(item); } public int Count { get { return currentItemCount; } } public bool Contains (T item ) { return Equals(items[item.HeapIndex], item); } void SortDown (T item ) { while (true ) { int childIndexLeft = item.HeapIndex * 2 + 1 ; int childIndexRight = item.HeapIndex * 2 + 2 ; int swapIndex; if (childIndexLeft < currentItemCount) { swapIndex = childIndexLeft; if (childIndexRight < currentItemCount) { if (items[childIndexLeft].CompareTo(items[childIndexRight]) < 0 ) { swapIndex = childIndexRight; } } if (item.CompareTo(items[swapIndex]) < 0 ) { Swap(item, items[swapIndex]); } else { return ; } } else { return ; } } } void SortUp (T item ) { int parentIndex = (item.HeapIndex - 1 ) / 2 ; while (true ) { T parentItem = items[parentIndex]; if (item.CompareTo(parentItem) > 0 ) { Swap(item, parentItem); } else { break ; } parentIndex = (item.HeapIndex - 1 ) / 2 ; } } void Swap (T itemA, T itemB ) { items[itemA.HeapIndex] = itemB; items[itemB.HeapIndex] = itemA; int itemAIndex = itemA.HeapIndex; itemA.HeapIndex = itemB.HeapIndex; itemB.HeapIndex = itemAIndex; } } public interface IHeapItem <T > : IComparable <T >{ int HeapIndex { get ; set ; } }
贪吃蛇
存储
显示
动画
Wander
生长
决策