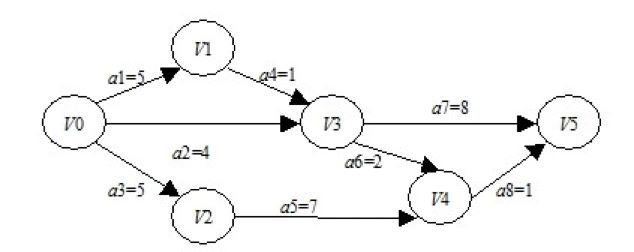
在一个有向无环图(DAG)中,有节点Vertices,连接两个节点的叫做边Edges,每条边都有权重Weight,指定一个起点,一个终点和X个中间点,用C++编写程序,找出经过所有这些指定点的权重之和的前TopN条路径。需要自己设计图的数据结构,构造相应单元测试用例(可以用GoogleTest),用例要覆盖X为1个或者多个,N为1条或者多条,并能运行通过测试用例。
程序设计
题目已经给出足够多的信息,可以依此直接创建Graph类而无需进行需求分析。类图如下:
图的创建与修改
我希望创建一个尽可能动态的图,这个图可以在任意时候新增或者删除节点,也可以在任意时候增加或者去除某条边,或改变某条边的权重。
使用邻接矩阵来表示图,定义了结构Edge用来表示一条边,定义了结构Path用来表示一条寻得的路径。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #ifndef graph_hpp #define graph_hpp struct Edge { int from = 0 ; int to = 0 ; int weight = 0 ; }; struct Path { int weight; std::vector<int > pathpoint; }; class Graph {private : int _vertices_count; std::vector<std::vector<int >> _edges; public : Graph (int size, std::vector<std::vector<int >> edges) : _vertices_count(size), _edges(edges) {} Graph (int size = 0 ) { *this = Graph (size, std::vector<std::vector<int >>(size, std::vector <int >(size, 0 ))); } bool addVertices (int number) bool insertVertex (int index) bool removeVertex (int index) bool setEdge (Edge e) bool setEdge (std::vector<Edge> v) bool isDAG () std::vector<Path> findPath (int from, int to, std::vector<int > pathpoint) ; private : std::vector<bool > __visited; std::vector<int > __next; void DFS (int from, int to, std::vector<int > &pathpoint, std::vector<Path> &result) }; #endif
图有两个构造函数
指定图的大小和邻接矩阵
指定图的大小,邻接矩阵初始化为0
对于图的顶点来说,有三个方法对它们进行操作:
addVertices:在末尾添加指定数量的顶点,会扩充邻接矩阵的大小insertVertex:在指定位置插入一个顶点,会扩充邻接矩阵的大小removeVertex:删除指定位置的顶点,会减小邻接矩阵的大小
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 bool Graph::addVertices (int number) if (number <= 0 ) return false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < _vertices_count; i++) { _edges[i].resize (_vertices_count + number); } for (int i = 0 ; i < number; i++) { _edges.push_back (std::vector <int >(_vertices_count + number, 0 )); } _vertices_count += number; return true ; } bool Graph::insertVertex (int index) if (index < 0 || index > _vertices_count) return false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < _vertices_count; i++) { _edges[i].insert (_edges[i].begin () + index, 0 ); } _edges.insert (_edges.begin () + index, std::vector <int >(_vertices_count + 1 , 0 )); _vertices_count++; return true ; } bool Graph::removeVertex (int index) if (index < 0 || index >= _vertices_count) return false ; _edges.erase (_edges.begin () + index); for (int i = 0 ; i < _vertices_count-1 ; i++) { _edges[i].erase (_edges[i].begin () + index); } _vertices_count--; return true ; }
有两个方法操作图的边(setEdge),删除边即将边的权重设置为0:
使用一个Edge结构来修改边
使用一个Edge的vector批量设置边
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 bool Graph::setEdge (Edge e) if (e.from >= _vertices_count || e.from < 0 || e.to >= _vertices_count || e.to < 0 ) { return false ; } _edges[e.from][e.to] = e.weight; return true ; } bool Graph::setEdge (std::vector<Edge> v) bool result = true ; for (auto &e : v) { if (!setEdge (e)) result = false ; } return result; }
isDAG使用拓扑排序方法判断图中是否有环,即判断图是否为有向无环图。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 bool Graph::isDAG () __visited = std::vector <bool >(_vertices_count, false ); int cnt = 0 ; bool finished = false ; auto edges = _edges; while (!finished) { bool contain_zero_degree = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < _vertices_count && !__visited[i]; i++) { int degree = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < _vertices_count; j++) { if (edges[j][i] > 0 ) degree++; } if (!degree) { contain_zero_degree = true ; cnt++; __visited[i] = true ; for (int j = 0 ; j < _vertices_count; j++) { edges[i][j] = 0 ; } } } finished = !contain_zero_degree; } return cnt == _vertices_count; }
寻找路径
为了寻找符合要求的路径,最简单的思路是寻得所有路径,并做筛选:
使用DFS遍历图中不走回头路的所有路径
使用一个__next数组用来回溯路径节点
使用一个__visited数组用来标记已经访问过的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 std::vector<Path> Graph::findPath (int from, int to, std::vector<int > pathpoint) { std::vector<Path> result; __visited = std::vector <bool >(_vertices_count, false ); __next = std::vector <int >(_vertices_count, 0 ); DFS (from, to, pathpoint, result); return result; } void Graph::DFS (int from, int to, std::vector<int > &pathpoint, std::vector<Path> &result) __visited[from] = true ; if (from == to) { Path p = {}; int k = 0 ; while (k != to) { p.pathpoint.push_back (k); k = __next[k]; } p.pathpoint.push_back (k); for (int i = 0 ; i < p.pathpoint.size () - 1 ; i++) { p.weight += _edges[p.pathpoint[i]][p.pathpoint[i+1 ]]; } bool is_match = true ; for (auto m : pathpoint) { if (std::find (p.pathpoint.begin (), p.pathpoint.end (), m) == p.pathpoint.end ()) { is_match = false ; } } if (is_match) { result.push_back (p); } return ; } for (int j = 0 ; j < _vertices_count; j++) { if (__visited[j] == false && _edges[from][j] != 0 ) { __next[from] = j; DFS (j, to, pathpoint, result); __visited[j] = false ; } } }
实验
编写如下代码用来测试Graph类是否满足要求:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <iostream> #include "graph.hpp" using namespace std;void show_path (vector<Path> path) cout << path.size () << " paths in total. " << endl; for (auto p : path) { for (auto v : p.pathpoint) { cout << v << "->" ; } cout << " w: " << p.weight << endl; } cout << endl; } int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) Graph g (5 ) ; g.setEdge ({ {0 , 1 , 5 }, {0 , 3 , 4 }, {0 , 2 , 5 }, {1 , 3 , 1 }, {2 , 4 , 7 }, {3 , 4 , 2 } }); g.addVertices (1 ); g.setEdge ({3 , 5 , 7 }); g.setEdge ({4 , 5 , 1 }); auto path = g.findPath (0 , 5 , {3 }); show_path (path); path = g.findPath (0 , 5 , {}); show_path (path); path = g.findPath (0 , 5 , {1 , 4 }); show_path (path); cout << "DAG? " << g.isDAG () << endl; g.setEdge ({4 , 0 , 3 }); cout << "DAG? " << g.isDAG () << endl; return 0 ; }
得到输出如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 4 paths in total. 0->1->3->4->5-> w: 9 0->1->3->5-> w: 13 0->3->4->5-> w: 7 0->3->5-> w: 11 5 paths in total. 0->1->3->4->5-> w: 9 0->1->3->5-> w: 13 0->2->4->5-> w: 13 0->3->4->5-> w: 7 0->3->5-> w: 11 1 paths in total. 0->1->3->4->5-> w: 9 DAG? 1 DAG? 0
可以知道程序各部分运行正常。
按权重排序
对于“找出经过所有这些指定点的权重之和的前TopN条路径”,即“top k”问题,常用堆数据结构来解决,对应C++中即为priority_queue。
修改findPath方法,使其返回一个优先队列:std::priority_queue<Path> findPath(int from, int to, std::vector<int> pathpoint);
修改DFS方法中的实现,将路径保存到一个优先队列中。
修改Path结构,让其能够使用优先队列,具体来说是重载其<运算符:
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct Path { int weight; std::vector<int > pathpoint; friend bool operator <(Path p1, Path p2) { return p1.weight < p2.weight; } };
修改显示函数,使用优先队列的遍历方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void show_path (priority_queue<Path> path) cout << path.size () << " paths in total. " << endl; while (!path.empty ()) { Path p = path.top (); for (auto v : p.pathpoint) { cout << v << "->" ; } cout << " w: " << p.weight << endl; path.pop (); } cout << endl; }
再次运行程序,得到输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 4 paths in total. 0->1->3->5-> w: 13 0->3->5-> w: 11 0->1->3->4->5-> w: 9 0->3->4->5-> w: 7 5 paths in total. 0->1->3->5-> w: 13 0->2->4->5-> w: 13 0->3->5-> w: 11 0->1->3->4->5-> w: 9 0->3->4->5-> w: 7 1 paths in total. 0->1->3->4->5-> w: 9 DAG? 1 DAG? 0
可以看出路径已经被正确排序,问题得到解决。
使用 hash
注意到匹配路径是否符合要求的过程需要两层循环,时间复杂度比较高,所以考虑使用 hash,将原本O(n^2)的时间复杂度降低到O(n)。
元素筛选,第一反应想到效率非常高的 bloom filter ,最初的设想是将中间路径点设置为 bloom filter,然后匹配一遍寻得的所有路径,由于 bloom filter 的特性,所需要的路径一定在经过初级筛选之后的子集中,接着对子集做精确的匹配,就能找到筛选结果。
这里我们先不采用 bloom filter 的方式,留作以后与学长老师们讨论。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 void Graph::DFS (int from, int to, std::vector<int > &pathpoint, std::priority_queue<Path> &result) __visited[from] = true ; if (from == to) { std::unordered_set<int > s; for (auto point : p.pathpoint) { s.emplace (point); } bool is_match = true ; for (auto m : pathpoint) { if (s.find (m) == s.end ()) { is_match = false ; } } } }
Cmake
文件目录结构为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 . ├── CMakeLists.txt ├── include │ └── graph.hpp ├── main.cpp └── src └── graph.cpp
CMakeLists.txt内容为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.15 )project (assignment1)MESSAGE (STATUS "my first cmake project" )set (EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR} /build)include_directories (${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR} /include )add_library (graph STATIC ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR} /src/graph.cpp)add_executable (${PROJECT_NAME} main.cpp)target_link_libraries (${PROJECT_NAME} graph)target_link_libraries (${PROJECT_NAME} libgtest.a libgtest_main.a pthread)set (CMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS ON )set (CPACK_PROJECT_NAME ${PROJECT_NAME} )set (CPACK_PROJECT_VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION} )include (CPack)
Google test
加入 GTest 的测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 TEST (testCase, test0) { Graph g (6 ) ; g.setEdge ({ {0 , 1 , 5 }, {0 , 3 , 4 }, {0 , 2 , 5 }, {1 , 3 , 1 }, {2 , 4 , 7 }, {3 , 4 , 2 }, {3 , 5 , 7 }, {4 , 5 , 1 } }); EXPECT_EQ (g.findPath (0 , 5 , {3 }).size (), 4 ); } int main (int argc, char ** argv) testing::InitGoogleTest (&argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS (); }
执行如下指令:
1 2 3 4 5 mkdir build cd build cmake .. make ./assignment1
运行结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [==========] Running 1 test from 1 test suite. [----------] Global test environment set-up. [----------] 1 test from testCase [ RUN ] testCase.test0 [ OK ] testCase.test0 (0 ms) [----------] 1 test from testCase (0 ms total) [----------] Global test environment tear-down [==========] 1 test from 1 test suite ran. (0 ms total) [ PASSED ] 1 test.