计算几何 - C++ 库的调研
系列文章
《计算几何——算法与应用(第三版)》学习笔记1 - 扫描线(第1-4章)
《计算几何——算法与应用(第三版)》学习笔记2 - 空间索引(第5-7章)
番外篇
-> 计算几何 - C++ 库的调研
Boost C++ Libraries学习 - Geometry
Boost C++ Libraries学习 - Boost.Polygon (GTL)
Boost.Geometry
学习笔记:Boost C++ Libraries学习 - Geometry
License
Distributed under the
Boost Software License, Version 1.0.
特点
- 易于使用,资料多、文档齐全。
- 常见的几何操作都有,但更小众的需求可能不如 CGAL。
可视化调试
vscode 插件:Graphical Debugging
使用方法:在 Debug 界面会有 GRAPHICAL WATCH 栏(图中左下角),在里面点击“+”号,输入变量名即可,效果如下:

但由于 GDB 和 LLDB 不会输出变量的原始类型(例如使用了typedef关键字来定义类型名),所以需要告诉插件某个类型应该如何展示。方式就是在当前调试的项目根目录下建立*.json,文件名可以随意,然后填入如下格式的内容:
1 | { |
那么我如下的类型定义就可以被识别:
1 | namespace bg = boost::geometry; |
关于 json 文件的详细内容可以参考插件仓库下的 json 文件。
进一步来说 json 文件的放置位置也不一定是项目根目录,扩展设置里面可以设置 json 文件的寻找目录,以及可视化展示的投影方式,如下图:
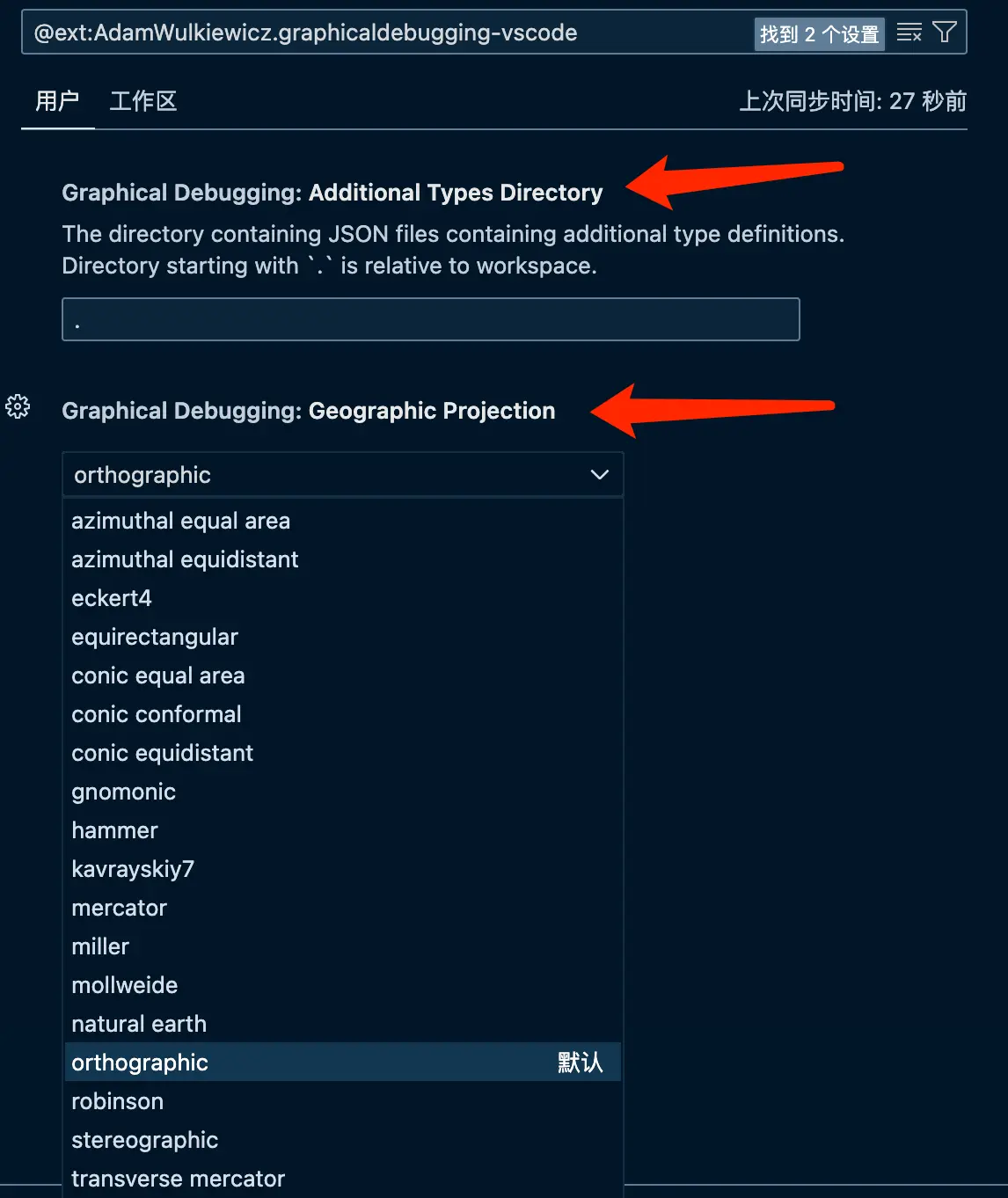
这里附上使用 boost.geometry 时候用到的 json 文件,可以在扩展设置里面把路径设置成./.vscode,然后放到这个路径下。最底下的aliases字段可以定义自己用typedef定义的类型别名。
1 | { |
GEOS
GEOS is a C/C++ library for computational geometry with a focus on algorithms used in geographic information systems (GIS) software. It implements the OGC Simple Features geometry model and provides all the spatial functions in that standard as well as many others. GEOS is a core dependency of PostGIS, QGIS, GDAL, Shapely and many others.
Spatial Model and Functions
- Geometry Model: Point, LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon, GeometryCollection
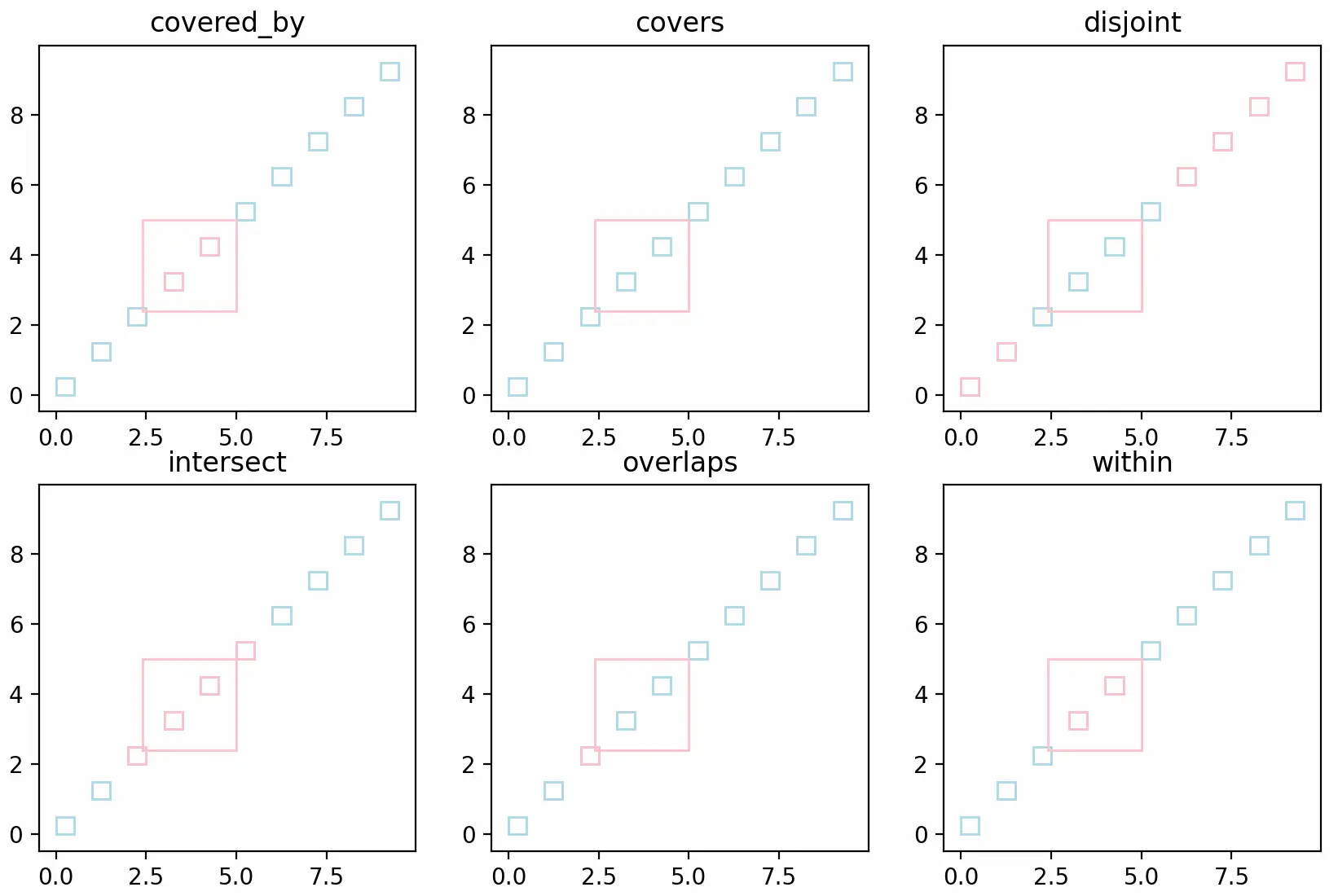
- Predicates: Intersects, Touches, Disjoint, Crosses, Within, Contains, Overlaps, Equals, Covers
- Operations: Union, Distance, Intersection, Symmetric Difference, Convex Hull, Envelope, Buffer, Simplify, Polygon Assembly, Valid, Area, Length,
- Prepared geometry (using internal spatial indexes)
- Spatial Indexes: STR (Sort-Tile-Recursive) packed R-tree spatial index
- Input/Output: OGC Well Known Text (WKT) and Well Known Binary (WKB) readers and writers.
License
GEOS is open source software available under the terms of GNU Lesser General Public License (
LGPL).
特点
- 主要专注于地理空间数据。
- 提供的更多的是空间操作和算法,但基本的几何操作也都有。
CGAL
CGAL is a software project that provides easy access to efficient and reliable geometric algorithms in the form of a C++ library. CGAL is used in various areas needing geometric computation, such as geographic information systems, computer aided design, molecular biology, medical imaging, computer graphics, and robotics.
The library offers data structures and algorithms like triangulations, Voronoi diagrams, Boolean operations on polygons and polyhedra, point set processing, arrangements of curves, surface and volume mesh generation, geometry processing, alpha shapes, convex hull algorithms, shape reconstruction, AABB and KD trees…
License
CGAL is distributed under a dual license scheme, that is under the
GNU GPL/LGPLopen source licenses, as well as undercommercial licenses.
特点
- 几何操作非常全面,功能强大。
- 学习成本相对较高。
- 有 License 的限制。
libigl
libigl is a simple C++ geometry processing library. We have a wide functionality including construction of sparse discrete differential geometry operators and finite-elements matrices such as the cotangent Laplacian and diagonalized mass matrix, simple facet and edge-based topology data structures, mesh-viewing utilities for OpenGL and GLSL, and many core functions for matrix manipulation which make Eigen feel a lot more like MATLAB.
License
libigl is primarily
MPL2licensed (FAQ). Some files contain third-party code under other licenses. We’re currently in the processes of identifying these and marking appropriately.
特点
- 主要专注的是离散几何和计算机图形学领域。
- 更多的提供的是三维模型的 mesh 网格处理。
OpenMesh
OpenMesh provides the following features:
- Representation of arbitrary polygonal (the general case) and pure triangle meshes (providing more efficient, specialized algorithms)
- Explicit representation of vertices, halfedges, edges and faces.
- Fast neighborhood access, especially the one-ring neighborhood (see below).
- Highly customizable :
- Choose your coordinate type (dimension and scalar type)
- Attach user-defined elements/functions to the mesh elements.
- Attach and check for attributes.
- Attach data at runtime using dynamic properties.
License
Latest Version (starting with 4.0) are Licensed under the
BSD 3 clauselicense
特点
- 主要专注于多边形网格处理和拓扑编辑。
GEOMETRIC TOOLS
Geometric Tools, a collection of source code for computing in the fields of mathematics, geometry, graphics, image analysis and physics. The engine is written in C++ 14 and, as such, has portable access to standard constructs for multithreading programming on cores. The engine also supports high-performance computing using general purpose GPU programming (GPGPU). Portions of the code are described in various books as well as in documents available at this site. The source code is freely downloadable, covered by the Boost License.
License
The GTL source code will be freely downloadable and subject to the
Boost License.
计算几何相关
- Boolean Operations on Intervals and Axis-Aligned Rectangles
- Clipping a Mesh Against a Plane
- Geodesics On Triangle Meshes
- Mesh Differential Geometry
- The Minimal Cycle Basis for a Planar Graph
- Polyline Reduction
- Tessellation of a Unit Sphere Starting with an Inscribed Convex Triangular Mesh
- Triangulation by Ear Clipping
特点
- 专注于计算机图形学。
- 易于使用。
- 相对来说功能可能更有限。